The Essential Tools of Orthopedic Surgeons: A Comprehensive Guide
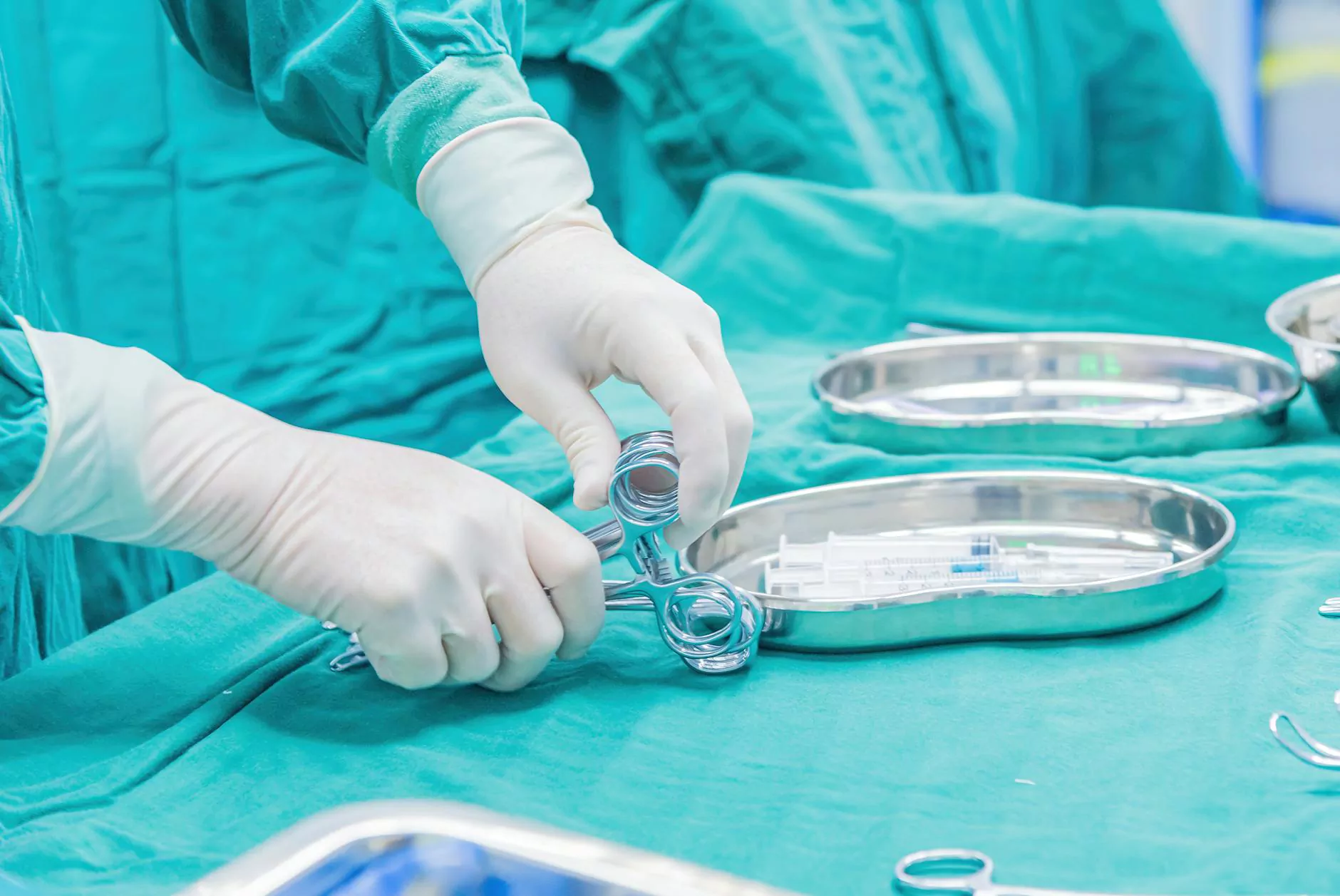
Orthopedic surgery is one of the most demanding fields in medicine, requiring precision and expertise to ensure successful patient outcomes. The success of these intricate surgical procedures heavily relies on the orthopedic surgeon tools employed during operations. In this article, we delve into the various tools that orthopedic surgeons use, their specific purposes, and the significance of utilizing high-quality medical supplies.
Understanding Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal conditions. This encompasses injuries and disorders involving bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. The tools utilized in this field are specially designed to assist surgeons in performing a variety of procedures—from joint replacements to fracture repairs. Understanding these tools is essential for professionals in the medical field as well as patients seeking information about their treatment options.
Types of Orthopedic Surgeon Tools
The tools used by orthopedic surgeons can be categorized into several groups based on their applications:
- Incisional Instruments: Used to make incisions in the skin and tissue.
- Grasping Instruments: Designed to hold or manipulate tissues and other instruments.
- Cutting Instruments: Essential for cutting through bones or tissues as required during surgery.
- Bone Fixation Devices: Includes screws, plates, and rods to stabilize fractured bones.
- Endoscopic Instruments: Used in minimally invasive surgeries to visualize and operate on internal structures.
1. Incisional Instruments
These instruments are crucial during the initial stage of any surgical procedure. They include:
- Scalpel: A surgical knife used for making incisions with precision.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors, particularly angled or serrated, are vital for cutting soft tissue.
- Electrocautery Devices: These devices assist in cutting through tissue while simultaneously coagulating blood vessels to minimize bleeding.
2. Grasping Instruments
Grasping instruments are designed to hold and manipulate tissues, thereby offering the surgeon better control during procedures. Key examples include:
- Forceps: Various types such as tissue forceps that allow for secure holding of tissues.
- Clamps: Used to occlude blood vessels or tissues temporarily during surgery.
3. Cutting Instruments
Cutting instruments are essential for precise cuts during surgeries. They include:
- Bone Saws: Specifically designed saws for cutting through bone. Electric or reciprocating saws are commonly used.
- Chisels and Osteotomes: These tools are used to shape and refine bone structures during procedures.
4. Bone Fixation Devices
Bone fixation devices play a vital role in stabilizing broken bones, allowing for proper healing. These devices include:
- Plates and Screws: Used to secure bones in place during the healing process.
- Intramedullary Nails: Metal rods inserted into the bone to support and stabilize fractures.
5. Endoscopic Instruments
Minimally invasive surgeries have gained popularity due to benefits such as reduced recovery times. Endoscopic instruments allow surgeons to operate through small incisions using:
- Endoscopes: Tools equipped with a camera to visualize internal structures in real-time.
- Trocar Instruments: Sharp-pointed tools that create entry points for other surgical instruments.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Surgeon Tools
Quality matters significantly in the performance and efficacy of orthopedic surgeon tools. Surgeons must have access to reliable, durable devices that minimize the risk of complications during procedures. The right tools not only provide better outcomes but also enhance the confidence of the surgical team. Here are some factors to consider when selecting tools:
- Material Quality: Stainless steel is often preferred for its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Manufacturer Reputation: It is crucial to choose tools from reputable manufacturers known for their quality and reliability.
- Ergonomics: Instruments designed for comfort and ease of use reduce fatigue during long surgeries.
- Certifications: Tools should meet safety and efficacy standards as established by organizations such as FDA or CE marking.
The Role of Technology in Orthopedic Surgery
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery, leading to the development of specialized orthopedic surgeon tools that enhance precision and patient care. Notable innovations include:
- Robotic Surgery Systems: These systems allow for greater precision in surgical procedures, resulting in minimally invasive techniques.
- 3D Printing: Custom prosthetics and surgical instruments can now be made, tailored to individual patient needs.
- Image-Guided Surgery: Integrating imaging technology helps surgeons visualize anatomy in real time, facilitating accurate cuts and placements.
Maintaining Orthopedic Surgeon Tools
Proper maintenance of orthopedic tools is crucial for ensuring their longevity and efficacy. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Cleaning: Instruments should be cleaned immediately after use to prevent contamination and corrosion.
- Sterilization: Autoclaving is often used to ensure instruments are free from any microbial life.
- Inspection: Regular checks for wear and tear help in identifying instruments that may need to be repaired or replaced.
Conclusion
In the world of orthopedic surgery, the tools at a surgeon's disposal are as crucial as the skills they possess. From basic instruments for making incisions to advanced robotic systems that enhance surgical precision, understanding and utilizing high-quality orthopedic surgeon tools is essential for successful patient outcomes. As the field continues to evolve with technological advancements, staying updated with the latest tools and techniques is imperative for medical professionals.
For quality medical supplies and innovative tools, visit New Med Instruments, where you can find a comprehensive range of orthopedic tools that meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.